Caution: Federal (USA) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Prior to use, please refer to the Instructions for Use for complete product indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions, potential adverse events, and detailed instructions for use.
Indication For Use
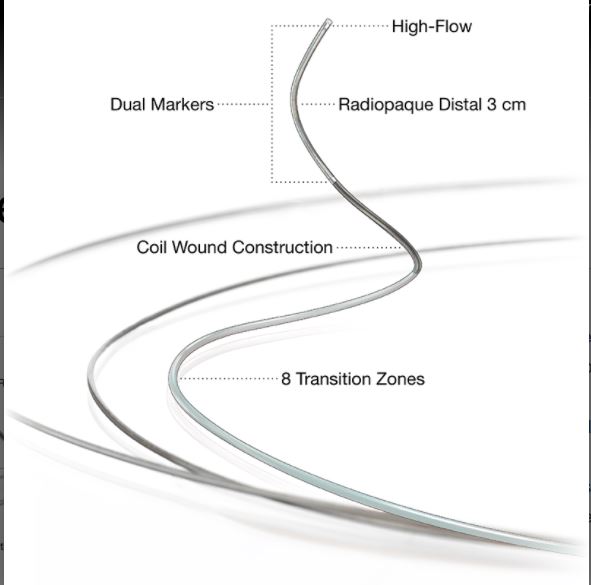
The Penumbra Delivery Microcatheters are intended to assist in the delivery of diagnostic agents, such as contrast media, and therapeutic devices, such as occlusion coils to the peripheral and neuro vasculature.
Contraindications
There are no known contraindications.
Warnings
The Penumbra Delivery Microcatheters should only be used by physicians who have received appropriate training in interventional techniques.
Precautions
• The devices are intended for single use only. Do not resterilize or reuse. Resterilization and/or reuse may result in ineffective catheter coating lubrication, which may result in high friction and the inability to access the target location.
• Do not use kinked or damaged devices. Do not use open or damaged packages. Return all damaged devices and packaging to the manufacturer/distributor.
• Use prior to the “Use By” date.
• Use the Penumbra Delivery Microcatheters in conjunction with fluoroscopic visualization.
• Do not advance or withdraw the Penumbra Delivery Microcatheters against resistance without careful assessment of the cause using fluoroscopy. If the cause cannot be determined, withdraw the device. Moving or torquing the device against resistance may result in damage to the vessel or device.
• Maintain a constant infusion of an appropriate flush solution.
• If flow through the device becomes restricted, do not attempt to clear the lumen by infusion. Remove and replace the device.
Potential Adverse Events
Possible complications include, but are not limited to, the following:
acute occlusion; hematoma or hemorrhage at access site; death; intracranial hemorrhage; hemorrhage; infection (at access site); distal embolization; ischemia (cardiac and/or cerebral); embolus (air, foreign body, thrombus, plaque); aneurysm perforation; false aneurysm formation; neurological deficits including stroke; vessel spasm, thrombosis, dissection, perforation or rupture; air embolism; emboli.