Manufacturer > Terumo Interventional Systems > Devices > ANGIO-SEAL® VIP Vascular Closure Device
ANGIO-SEAL® VIP Vascular Closure Device
Device-Type
Closure Devices
Manufacturer
Terumo Interventional Systems
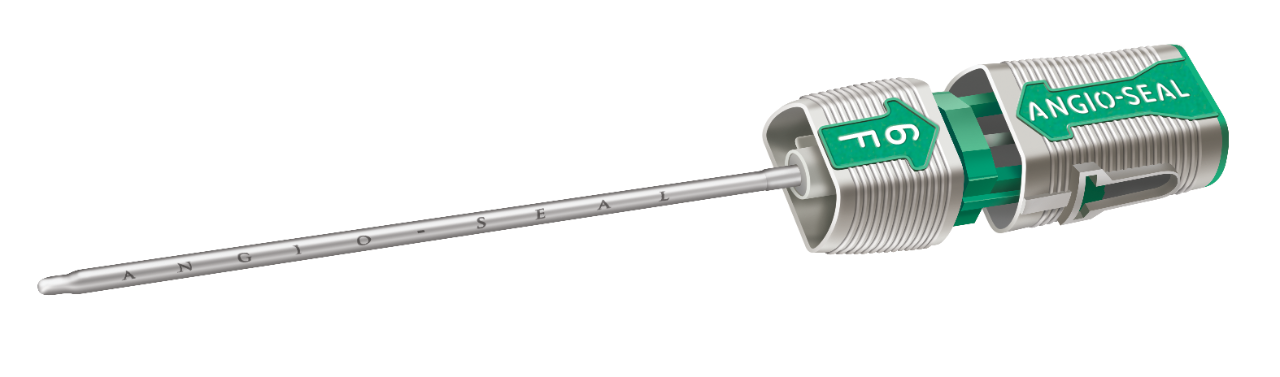
The Angio-Seal™ VIP Vascular Closure Device consists of the Angio-Seal VIP device, an insertion sheath, an arteriotomy locator (modified dilator) and a guidewire. The Angio-Seal VIP device is composed of an absorbable collagen sponge and a specially designed absorbable polymer anchor that are connected by an absorbable self-tightening suture (STS). The device seals and sandwiches the arteriotomy between its two primary members, the anchor and collagen sponge. Hemostasis is achieved primarily by the mechanical means of the anchorarteriotomy-collagen sandwich, which is supplemented by the coagulation-inducing properties of the collagen. The device is contained in a delivery system that stores and then delivers the absorbable components to the arterial puncture. The delivery system features a Secure Cap that facilitates proper technique for delivery and deployment of the absorbable unit. The implanted components of the device are MRI Safe. The product is not made with natural rubber latex.
INDICATIONS
The Angio-Seal device is indicated for use in closing and reducing time to hemostasis at the femoral arterial puncture site in patients who have undergone diagnostic angiography procedures or interventional procedures using an 8 French or smaller procedural sheath for the 8F Angio-Seal device and a 6 French or smaller procedural sheath for the 6F Angio-Seal device. The Angio-Seal device is also indicated for use to allow patients who have undergone diagnostic angiography to ambulate safely as soon as possible after sheath removal and device
The device creates a mechanical seal by sandwiching the arteriotomy between a bioabsorbable anchor and collagen sponge, which dissolve in 60 to 90 days.
Three bioabsorbable components actively seal the arteriotomy:
- Anchor: Bioabsorbable co-polymer anchor placed against the inside of the vessel wall
- Collagen: Placed on top of the arteriotomy in the tissue tract
- Suture: Cinches the anchor and collagen together to form a secure seal
STEP-BY-STEP INSTRUCTIONS
LOCATE THE ARTERY
- Exchange the procedure sheath with the Angio-Seal locator system.
- Blood flow through the locator visually confirms proper sheath position in the artery.
SET THE ANCHOR
- Insert the Angio-Seal VIP device into the sheath until you hear a “click.”
- Gently pull back on the locking cap until you hear another “click.”
- The anchor is now locked in place and device is ready to be deployed.
SEAL THE PUNCTURE
- Gently pull back on the Angio-Seal VIP device until the suture has stopped spooling.
- Maintain upward tension on the device and gently advance the compaction tube until resistance is felt.
- Cut the suture and remove the device.
Features and Benefits
Safety informations
Potential adverse events
Device Documents
Questions & Answers